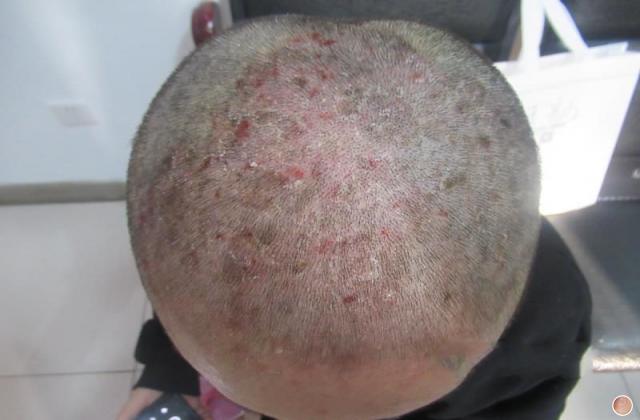
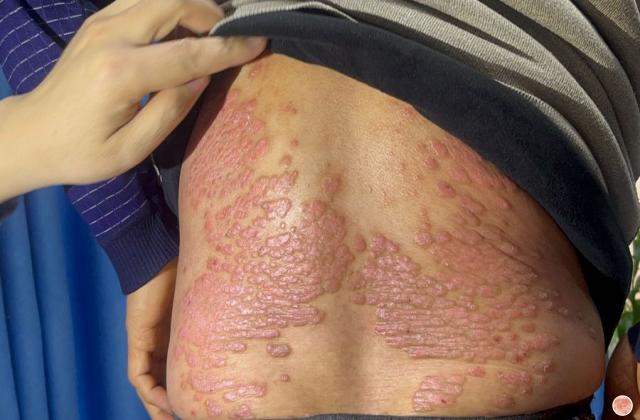
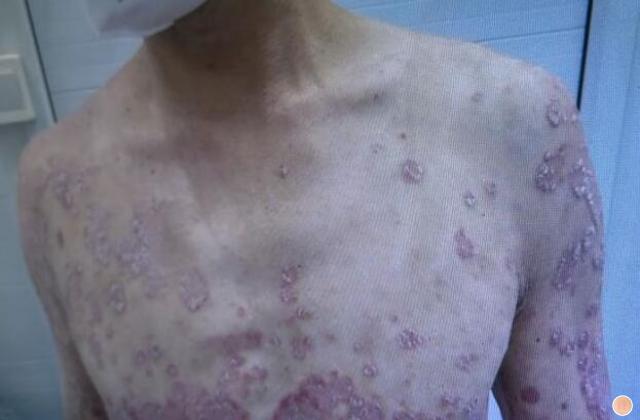
血热型银屑病英文
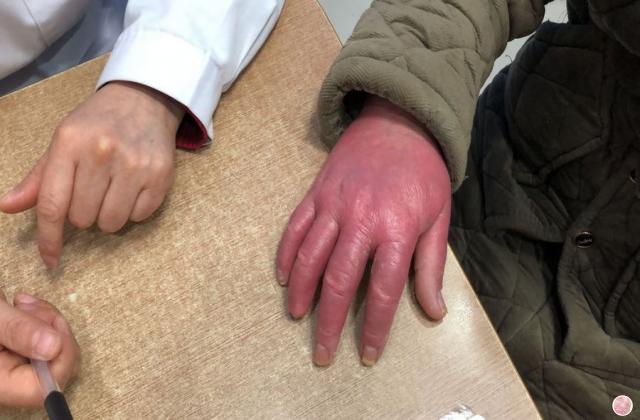
Blood Heat Psoriasis

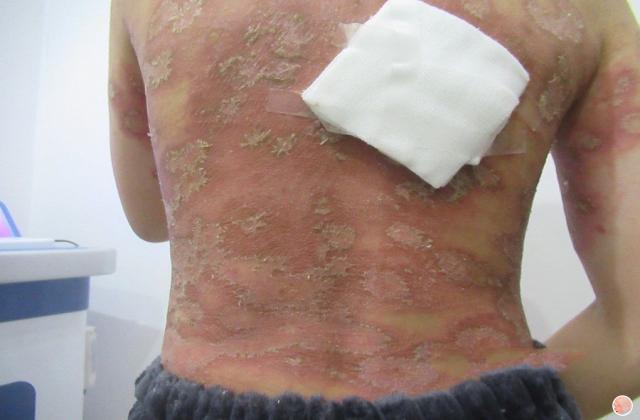
Blood Heat Psoriasis is a rare and severe form of psoriasis that is characterized by the accumulation of heat and toxins in the body. This condition is also known as Erythrodermic Psoriasis, and it affects only a small percentage of people diagnosed with psoriasis.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Blood Heat Psoriasis include:
1. Extreme Itching: The skin becomes intensely itchy, causing significant discomfort.
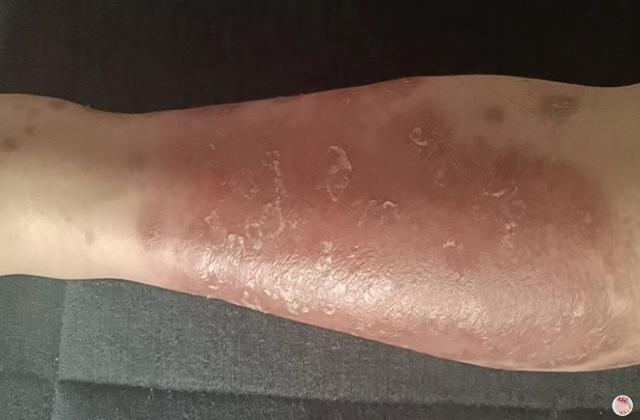
2. Skin Redness: The skin becomes red and inflamed, and there may be a burning sensation.
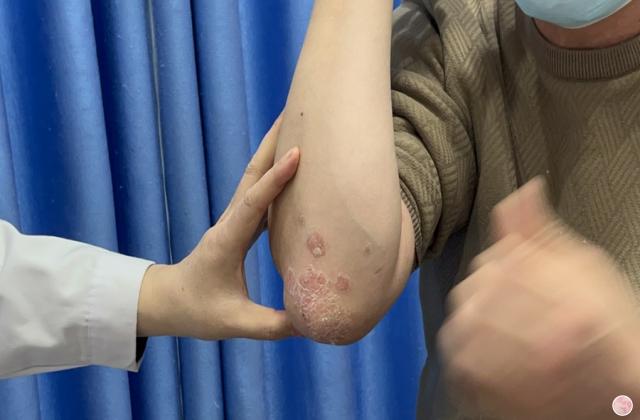
3. Skin Peeling: The skin may start to peel off in large scales or flakes, leading to skin sensitivity and pain.
4. Raised Bumps: The skin may develop raised bumps or papules, which can make the skin have a rough texture.
5. Fluid Retention: The skin may retain fluid, leading to swelling and edema.
6. Fever: Some people may develop fever, which can cause further discomfort and fatigue.
Causes
The exact cause of Blood Heat Psoriasis is not yet known. However, some factors that may contribute to the development of this condition include:
1. Stress: Emotional stress can trigger psoriasis flares in some people.
2. Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroid withdrawal, lithium, and antimalarial drugs, can cause psoriasis flares.
3. Trauma: A physical injury, such as a cut, scrape, or sunburn, can trigger psoriasis flares.
4. Infections: Streptococcal infections, such as strep throat, can trigger psoriasis flares.
5. Weather Changes: Extreme weather conditions, such as hot or cold climate, can trigger psoriasis flares.
Treatment
Blood Heat Psoriasis requires immediate medical attention because it can lead to life-threatening complications. Treatment options may include:
1. Topical Treatments: Topical creams, ointments, and gels may help relieve itching, inflammation, and scaling.
2. Systemic Medications: Oral or injectable medications can reduce inflammation throughout the entire body.
3. Light Therapy: Phototherapy or UVB therapy can help improve skin symptoms by reducing inflammation.
4. Immunosuppressants: These drugs suppress the immune system and can reduce inflammation and swelling.
5. Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to manage fluid retention, stress, and other complications.
Prevention
To prevent Blood Heat Psoriasis symptoms from worsening or triggering flares, individuals should:
1. Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that can cause psoriasis flares, such as stress, infections, and injuries.
2. Protect Skin: Protect the skin from excessive heat, cold, and sunlight exposure.
3. Moisturize Skin: Keep the skin moist and hydrated with moisturizers and emollients.
4. Manage Stress: Practice stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
5. Follow Treatment Plans: Follow the treatment plan prescribed by the healthcare provider to manage symptoms and prevent complications.